Implementing Salesforce B2B Commerce is a strategic investment that can reshape how a company manages digital channels, supports sales teams, and serves other businesses online. Yet the platform’s depth, covering catalog management, account hierarchies, contract pricing, integrations, and order workflows, makes the rollout far more complex than many organizations anticipate. Missteps in data structure, integrations, or user experience often slow adoption, limit operational efficiency, and weaken customer satisfaction.
Research from McKinsey shows that B2B buyers now use 10 or more digital channels during their purchasing journey - a sign that poor implementation directly affects revenue and retention. When Salesforce Commerce Cloud and connected systems such as Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and ERP platforms are not aligned, sales representatives lose access to accurate contract pricing, customers struggle to reorder, and support teams face a growing volume of avoidable issues.
This guide outlines the most common mistakes in Salesforce B2B Commerce implementations that hinder companies' progress. It also provides detailed recommendations and practical steps to help businesses build a scalable online store, optimize business processes, and deliver a buying experience that drives repeat customers and long-term growth.
Common Salesforce B2B Commerce Implementation Mistakes

Mistake 1: Poor Product & Catalog Data Structure
A large share of failed Salesforce B2B Commerce implementation projects can be traced back to weak product and catalog foundations. B2B buyers depend on accurate product data, account-specific pricing, and logical category structures to complete large volume purchases efficiently. When this data is inconsistent or poorly organized, both performance and customer experience suffer.
Symptoms of Poor Data Structure
- Disorganized catalogs that force buyers to search through irrelevant categories or outdated product lists.
- Incorrect pricing tiers that expose the wrong contract pricing or discount levels to key accounts.
- Slow site performance, especially when product data is bloated with unnecessary attributes or duplicate values.
Recent research highlights how critical high-quality product data has become for digital commerce. According to the Akeneo B2C Survey 2025, 30% of consumers report dissatisfaction with the comprehensiveness of product data, more than double the rate from two years earlier.
Additionally, 40% of consumers returned a product in the past year due to inaccurate product information, underscoring the financial impact of poor product content. While the study focuses on B2C, the implications in B2B environments, where orders are higher value and transactions depend heavily on technical specifications, are even more significant.
How to Avoid It
- Conduct a product data audit: Review product data across existing systems, including ERP platforms, CRM, and legacy catalogs. Identify duplicate SKUs, missing attributes, outdated specifications, and inconsistent naming. Clean data accelerates site performance and improves search relevance.
- Standardize categories, attributes, and price books: Align product families, category hierarchies, and standardized attributes before launching the online store. Create a structured approach for contract pricing, price books, and account-specific pricing, so customers and sales representatives always access accurate values.
- Use product workspace and pricing workspace effectively: Salesforce Commerce Cloud provides dedicated tools for product and pricing management. Product Workspace helps internal teams maintain product quality, upload high-quality images, and track product data completeness. Pricing Workspace centralizes pricing tiers, supports contract pricing, and minimizes mismatches across digital channels.
Mistake 2: Underestimating Integration Complexity
Integrations are the backbone of any Salesforce B2B Commerce implementation, particularly for companies that rely on ERP platforms, Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and Salesforce Order Management to support operational workflows.
When integrations are incomplete or poorly designed, the entire commerce experience becomes unstable. Pricing, inventory, and order data must move reliably between backend systems and Salesforce Commerce Cloud. Any gap in this flow disrupts business processes and slows down sales activities.
Symptoms of Integration Issues
- ERP ↔ Commerce sync failures that leave outdated product data, incorrect stock levels, or incomplete order details
- Order delays when submissions cannot be processed or validated across systems
- Pricing mismatches caused by inconsistent data between price books, ERP price lists, or contract pricing models
The latest MuleSoft Connectivity Benchmark Report highlights how widespread these issues have become. According to Salesforce research, 95% of IT leaders struggle to integrate data across systems, and only 29% of applications are connected on average.
How to Avoid It
- Use MuleSoft or middleware for reliable integration: Middleware platforms help organizations centralize and orchestrate data flows between Salesforce Commerce Cloud and backend systems. They reduce the dependency on point-to-point integrations that often break during scale or platform upgrades.
- Map data flows before implementation: Documenting the movement of product data, customer hierarchies, pricing books, and order details across all systems helps identify gaps that may affect order management or customer satisfaction. This step also aligns internal teams on ownership, data sources, and compliance requirements.
- Test large volumes of pricing, orders, and inventory updates: B2B storefronts must handle frequent contract pricing changes, complex account hierarchies, repeat orders, and large-volume transactions. Testing high data loads reduces the risk of failures during peak demand and validates how integrations behave under real conditions.
Mistake 3: Ignoring B2B Buyer Experience
Many companies approach Salesforce B2B Commerce implementation as a technology project rather than a buyer-focused initiative. B2B customers expect fast ordering, accurate pricing, and intuitive navigation that supports their daily workflows. When storefronts are difficult to use, sales teams lose revenue, customer loyalty declines, and buyers return to offline channels.
Symptoms of a Poor Buyer Experience
- Low re-order rate because buyers cannot quickly access past orders, saved carts, or custom catalogs
- High abandonment when the buying process becomes too complex, especially for large volume purchases
- Confusing navigation that forces users to browse irrelevant categories or struggle with poorly structured product catalogs
The importance of buyer experience continues to grow. A Gartner study found that 77% of B2B buyers reported their last purchase was difficult or complex. In parallel, Salesforce research shows 85% of business buyers expect the same level of experience as B2C.
How to Avoid It
- Personalize catalogs, pricing, and recommendations: Use account management tools and buyer groups to deliver custom catalogs, account-specific pricing, and AI-driven product suggestions. Personalization reduces friction and helps buyers locate relevant products quickly. For organizations with complex account hierarchies or contract pricing models, personalized experiences also reduce errors and support accurate order management.
- Optimize mobile ordering: According to Gartner, over 60% of B2B buyers prefer mobile for research and transactions. Many field sales representatives and on-site technicians depend on easy online access through mobile devices to reorder products, check order history, or review contract pricing. Optimizing mobile UX (search, navigation, product images, and checkout) directly improves repeat purchases and reduces abandonment.
- Offer quick-order tools, favorites, reorder lists, and custom carts: B2B buyers often manage recurring purchases, bulk orders, and multi-SKU transactions. Quick-order interfaces, saved lists, custom carts, and reorder buttons cut the time buyers spend navigating the storefront. Access to past invoices, order confirmations, and purchase history also streamlines procurement and reduces support requests.
Mistake 4: Not Utilizing Einstein AI & Personalization
Personalization is no longer optional in B2B commerce. Buyers expect relevant product recommendations, accurate contract pricing, and tailored content that reflects their purchase history and business needs. When companies overlook Einstein AI capabilities in Salesforce B2B Commerce Cloud, the storefront becomes static, conversions drop, and buyers spend more time searching for products they reorder frequently.
Symptoms of Limited Personalization
- Static product suggestions that fail to reflect industry, account, or historical buying behavior
- Poor conversions due to irrelevant product recommendations or generic catalog views
The pressure for relevance is rising quickly. According to Accenture, 84% of B2B executives say they cannot react fast enough to their customers’ changing needs, and 73% of people expect companies to understand their unique requirements. In addition, 93% of CMOs expect AI to reshape their relationship with customers, highlighting the growing expectation for personalized experiences across digital channels.
How to Avoid It
- Enable Einstein recommendations: Einstein analyzes browsing patterns, purchase history, and related products to deliver relevant recommendations. This supports higher average order value and reduces the effort buyers spend searching through extensive product catalogs.
- Use AI to analyze contract-based purchasing patterns: Contract pricing, negotiated discounts, and account-specific preferences play a major role in B2B transactions. AI models detect recurring purchasing behavior (bundles, seasonal patterns, complementary items) and surface the right products for each buyer group.
- Automate product suggestions based on user behavior: Automating suggestions based on search queries, category visits, and past orders provides a more intuitive experience. This also reduces manual merchandising work for internal teams, especially when managing large product catalogs or complex account hierarchies.
Mistake 5: Over-Customizing the Platform
B2B organizations often try to replicate legacy workflows, ERP logic, or long-standing internal processes inside Salesforce B2B Commerce Cloud. This leads to heavy customization that goes far beyond what the platform is designed to support. While custom features may offer short-term convenience, they introduce long-term risks, delay upgrades, slow performance, and increase reliance on specialized developers.
Symptoms of Over-Customization
- Difficult upgrades because core components or templates were overridden rather than extended
- High maintenance cost as internal teams spend more time troubleshooting custom code instead of using built-in capabilities
- Performance issues caused by scripts, custom logic, or non-standard data models that add unnecessary load to the storefront
Industry research reinforces the problem. MuleSoft’s Connectivity Benchmark shows that 39% of IT teams’ time is spent building and testing custom integrations instead of improving core business capabilities, and 86% of IT leaders expect workloads to rise. Over-customization multiplies this burden and slows innovation.
How to Avoid It
- Follow the Salesforce clicks-not-code approach: Use declarative tools before considering custom development. Salesforce provides configuration options for pricing, catalogs, buyer groups, account hierarchies, and permissions that meet most B2B use cases without requiring custom code.
- Stick to the B2B Commerce reference architecture: The reference architecture outlines how to manage product data, pricing, checkout flows, and integrations in a scalable way. Adhering to this model keeps the storefront maintainable, improves site stability, and allows businesses to roll out new capabilities faster.
- Build modular customizations, not platform overrides: When customization is necessary, build extensions that do not conflict with core components. Modular design allows teams to replace or update individual features without disrupting the entire storefront. This reduces upgrade risk and supports smoother performance across digital channels.
Mistake 6: Failure to Optimize Site Performance
Performance plays a critical role in Salesforce B2B Commerce. Buyers expect fast load times, accurate search results, and uninterrupted access to product catalogs and pricing. When performance is weak, even well-designed storefronts experience lower conversion rates, higher abandonment, and increased support inquiries. For B2B companies managing large catalogs, complex pricing structures, and high-volume transactions, performance issues directly affect revenue and operational efficiency.
Symptoms of Poor Performance
- Slow page loads, especially on product listing pages with large catalogs or complex filtering
- Timeout errors during checkout or when loading account-specific pricing
- Poor search relevance caused by unoptimized indexes or inconsistent product data
Performance is a known challenge across digital commerce. Salesforce’s own performance guidance notes that unoptimized media, inefficient queries, and excessive client-side scripts are among the top contributors to slow storefronts. This is especially problematic in B2B environments where product catalogs can reach tens of thousands of SKUs.
How to Avoid It
- Enable CDN caching: A content delivery network distributes assets worldwide, reducing latency for buyers in different regions. CDN caching is essential for B2B companies expanding into new markets or supporting customers across multiple countries with currency support and regional catalogs.
- Use Lightning Web Runtime best practices: LWR enables faster rendering and better control over storefront performance, but only when used correctly. Best practices include minimizing client-side logic, reducing unnecessary network calls, and leveraging built-in caching capabilities for product data and account-specific pricing.
- Optimize images, rich media, and search indexes: High-quality images are essential for product clarity, but uncompressed files slow down page loads. Use appropriate formats, compression, and responsive sizing for both desktop and mobile devices. In parallel, optimize search indexes by tuning synonyms, facets, and filters so queries return relevant results quickly, even across large catalogs.
Mistake 7: Neglecting User Roles & Permissions
User roles, account structures, and permissions form the backbone of Salesforce B2B Commerce. Buyers expect accurate pricing, relevant catalogs, and access aligned with their position within the organization, whether they are procurement managers, field technicians, or finance specialists reviewing invoices. When roles and permissions are poorly configured, the storefront exposes sensitive data, displays incorrect pricing, or grants access to products and catalogs that a buyer should never see.
Symptoms of Weak Role & Permission Management
- Wrong pricing shown, especially for accounts with contract pricing or negotiated tiers
- Access to restricted catalogs, leading to confusion, compliance issues, or unauthorized product visibility
- Security issues when users gain access to functions or data they are not intended to view
When roles are misconfigured, personalization breaks, ordering becomes inconsistent, and internal teams face a surge in support tickets related to catalog visibility and pricing discrepancies. In B2B environments, where account hierarchies, approval workflows, and multi-level permissions are common, small configuration errors can disrupt the entire buying process.
How to Avoid It
- Map B2B buyer personas: Identify how different buyers interact with the system: procurement teams, operations managers, sales reps, finance administrators, and field technicians all have distinct tasks. Mapping these personas early helps define permissions, catalog access, and pricing rules that reflect real business processes.
- Use buyer groups, org accounts, and contract-based access: Salesforce B2B Commerce provides robust tools to control visibility and pricing. Buyer groups allow companies to segment access by region, business unit, or purchasing role. Org accounts support complex account hierarchies, while contract-based access ensures each account sees the correct price books and catalogs. These capabilities reduce errors and maintain consistency across digital channels.
- Perform recurring permission audits: Over time, accounts evolve, new customers come onboard, and internal teams adjust business rules. Conduct periodic audits to confirm permissions still match current business needs. Reviewing user roles, contract pricing access, and catalog visibility reduces security risks and prevents operational issues that can stall transactions.
Mistake 8: Inadequate Testing Before Launch
Testing is often compressed into the final stages of a Salesforce B2B Commerce implementation, which leads to issues that surface only after customers begin using the storefront. B2B environments involve complex pricing structures, custom catalogs, integrations with ERP systems, and multi-level account hierarchies. Without extensive testing, these elements fail under real-world conditions and disrupt the buying process.
Symptoms of Insufficient Testing
- Broken checkout due to incomplete validation rules, payment configuration issues, or integration failures
- Pricing mismatches when contract pricing, price books, or account-specific discounts are not tested across all buyer profiles
- Integration bugs that affect inventory sync, order submissions, or order confirmations
How to Avoid It
- Use full UAT across all buyer roles: Test as a procurement manager, technician, finance reviewer, distributor, and internal sales rep. Each role accesses different catalogs, pricing, and approval workflows. Full UAT helps teams identify real scenarios buyers encounter across their business processes.
- Load testing for large catalogs (50k+ SKUs): Many B2B companies operate with extensive product catalogs that strain search, filters, and caching if not optimized. Load testing validates search performance, category navigation, and pricing retrieval under real catalog sizes.
- Simulate high order volumes: Test thousands of concurrent orders, inventory updates, and pricing updates. High-volume simulations reveal integration timeouts and bottlenecks that are difficult to detect with small-scale tests.
Mistake 9: Missing Post-Launch Monitoring & Optimization
A Salesforce B2B Commerce rollout does not end at go-live. The storefront must be continually monitored to track order performance, search behavior, pricing accuracy, and customer engagement patterns. Companies that skip post-launch optimization often see declines in conversion rates and a rising volume of support tickets as the site scales.
Symptoms of Poor Post-Launch Monitoring
- Decline in conversion rate as search relevance falls or browsing friction increases over time
- Order errors caused by evolving ERP logic, pricing changes, or unmonitored integrations
- High support tickets related to login issues, catalog visibility, permissions, or pricing discrepancies
How to Avoid It
- Implement dashboards for orders, cart abandonment, and site performance: Monitor patterns in checkout failures, page load times, and abandoned carts. Dashboards help internal teams identify areas that need improvement, from payment issues to slow product listing pages.
- Monitor search logs and refine synonyms: Search behavior shifts as new products are added or new customers enter the system. Reviewing search logs helps internal teams refine synonyms, adjust attributes, and fix gaps in product data that affect discoverability.
- Use predictive analytics for ongoing optimization: Predictive models highlight early signals of churn, identify declining product performance, and surface opportunities to improve recommendations or catalog organization. This helps companies maintain strong customer satisfaction and support repeat customers across digital channels.
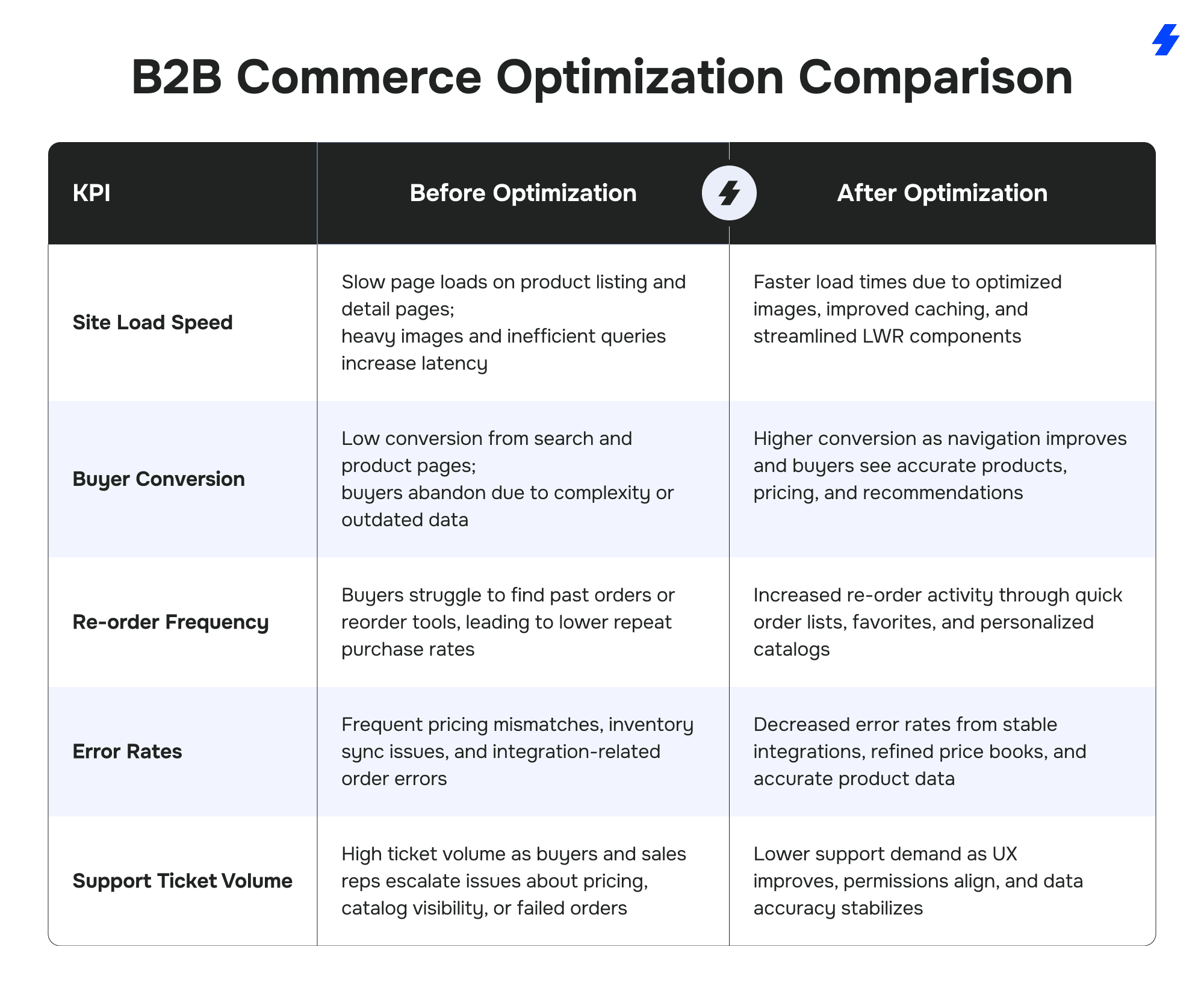
B2B Commerce “Before & After Optimization” Comparison
B2B Commerce Architecture Overview
A successful Salesforce B2B Commerce rollout depends on a clear architecture that connects the online store with all critical backend systems. At a high level, a modern B2B commerce landscape typically includes the following components:
Salesforce B2B Commerce (Storefront Layer)
- Hosts your B2B ecommerce storefronts for other businesses
- Exposes product catalogs, contract pricing, and account specific pricing
- Handles carts, checkout, and buyer self service (order history, access past invoices, order confirmations)
- Integrates with Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, and Revenue Cloud for a unified customer experience
ERP and Core Backend Systems
- Source of truth for financials, inventory, and often base product data
- Manages tax logic, fulfillment rules, and sometimes contract pricing for key accounts
- Connects to B2B Commerce through middleware (for example MuleSoft) for data migration, ongoing sync of product data, and order status updates
Inventory and Pricing Systems
- Real-time or near real time inventory feeds to the storefront
- Centralized pricing engine for for complex contract pricing discount schedules, and large volume purchases
- Works with Salesforce price books and Salesforce CPQ to keep product data, price rules, and account management aligned
Order Management System (OMS)
- Often Salesforce Order Management or another dedicated OMS
- Orchestrates fulfillment, partial shipments, returns, and order splitting across warehouses
- Feeds order history and status back into the online store and Salesforce CRM so sales reps and sales teams have full visibility
Payment Gateways and Payment Options
- Connects to PSPs for card payments, account credit, purchase orders, and local payment options for new markets and multiple currencies
- Supports multiple currencies and region-specific compliance requirements
Experience and Analytics Layer
- Marketing Cloud for campaigns, journeys, and behavior based nurturing
- Analytics and custom reports to monitor performance, track average order value, buyer paths, and identify areas for improvement
- Search and recommendation services, including Einstein and headless or composable commerce setups where B2B Commerce exposes APIs for other digital channels and mobile devices
B2B Commerce Scoring Checklist
Use this scoring checklist to assess your Salesforce B2B Commerce implementation readiness. Each category reflects a critical area that influences performance, scalability, and customer satisfaction. Scoring each item from 1 (Needs major improvement) to 5 (Fully optimized) provides a realistic snapshot of your current state and helps identify priority areas for the next phase of your project.

Pre-Launch Audit Template
Use this audit as a practical checklist before going live with Salesforce B2B Commerce. It focuses on the highest risk areas: pricing, catalog quality, performance, UX, and permissions.
1. Pricing and Contract Validation
- All price books are linked to the correct accounts and account hierarchies
- Contract pricing rules are validated for key accounts and typical example customers
- Volume-based discounts, tiered pricing, and support contract pricing behave correctly in the cart
- Taxes, shipping charges, and fees are calculated accurately across regions and currencies
- Test orders for each major segment (distributors, dealers, direct customers) display the correct totals
2. Catalog and Product Data Accuracy
- Product categories, attributes, and filters reflect how buyers actually search and buy
- High-quality images are present for all visible products and render correctly on mobile devices
- Product descriptions, technical specs, and compliance requirements are complete and consistent
- Custom catalogs and account specific catalogs display only allowed products for each segment
- Search results and facets match expectations for important keywords and product families
3. Performance and Stability Testing
- Load tests executed with realistic data sets (for example 50k+ SKUs and large price books)
- Page load times for home, category, search, and product detail pages meet internal targets
- CDN caching is configured for static assets and dynamic pages where appropriate
- Stress tests run for high order volumes and concurrent users, including peak periods
- Error logs monitored during testing to catch timeout errors and integration failures
4. UX Review Across Devices
- Checkout flows validated for all major buyer roles, including guest, logged in, and key accounts
- Quick order, favorites, reorder lists, and saved carts function as expected
- Navigation labels and menu structure follow buyer terminology, not only internal naming
- Forms, tables, and order views are usable on mobile devices and tablets
- Content and calls to action support both new customers and existing repeat customers
5. Roles, Permissions, and Access Control
- Buyer groups aligned with real target audience segments (region, channel, role, partner type)
- Account specific pricing and custom catalogs tested for each buyer group
- Internal users (sales representatives, customer service, operations) see the correct tools and data
- Sensitive information such as cost fields or internal only SKUs is not exposed
- A recurring permission review process is documented for post launch governance
Best Practices by Industry
Manufacturing — High-Volume SKUs
Focus on powerful search, guided navigation, and quick-order tools to support technicians and buyers dealing with extensive product catalogs.
Wholesale & Distribution — Contract-Based Pricing
Use price book hierarchies, buyer groups, and account-specific catalogs to manage complex discount structures for key accounts.
CPG — Fast, Frequent Reordering
Enable saved carts, favorites, and reorder from history to streamline replenishment for high-frequency buyers.
Automotive & Aftermarket — Multi-Dealer Networks
Implement org-based access controls and account hierarchies to reflect dealer structures and restrict visibility to the appropriate catalogs and pricing.
Why Choose MagicFuse for B2B Commerce Implementation?
MagicFuse brings specialized expertise and a proven delivery model to complex Salesforce B2B Commerce projects. Our team combines technical depth, industry knowledge, and a strong focus on data quality, integrations, and buyer experience - key elements that determine long-term success in B2B commerce.

Certified Salesforce B2B Commerce Experts
Our consultants hold advanced Salesforce certifications and have hands-on experience implementing B2B Commerce, Salesforce B2B Commerce (including legacy B2B Commerce Cloud), and related Salesforce solutions across multiple industries.
Proven Track Record with Multi-Language, Multi-Currency Stores
We build scalable ecommerce storefronts for businesses operating across regions, currencies, and regulatory environments, supporting global growth without compromising performance or data accuracy.
Strong ERP + B2B Commerce Integration Experience
Our team excels at integrating Salesforce with ERP platforms, pricing engines, and backend systems. This ensures consistent product data, inventory availability, and contract pricing across all digital channels.
Deep UX Optimization Expertise
MagicFuse focuses on creating buying experiences that reduce friction, improve search accuracy, and support repeat purchasing. We design storefronts that align with buyer workflows, account structures, and complex B2B processes.
Ongoing Support and Performance Tuning
Post-launch, we monitor performance, optimize search, refine catalogs, and adjust integrations. Our managed services model helps businesses maintain high availability, reduce support tickets, and continually improve KPIs such as conversion rate and average order value.
Reach out to us today to discuss your goals, review your current setup, and explore how we can support your next stage of digital growth.
FAQs
Why is B2B Commerce implementation so complex compared to B2C?
B2B Commerce involves account hierarchies, contract pricing, custom catalogs, approval workflows, and large product catalogs—none of which exist at the same scale in B2C. Integrations with ERP, pricing engines, and order management systems add another layer of complexity, making B2B implementations significantly more demanding.
How long does a typical implementation take?
Most Salesforce B2B Commerce projects take 3–6 months, depending on catalog size, pricing complexity, number of integrations, and required customizations. Projects involving multiple regions or custom workflows can take longer, especially when data migration and ERP alignment are part of the scope.
What integrations are essential for B2B Commerce success?
The most important integrations typically include:
1 - ERP systems for product data, pricing, inventory, and order processing 2 - Salesforce CRM / Sales Cloud for account data and sales activities 3 - Salesforce Order Management or another OMS for fulfillment and order tracking 4 - Payment gateways for multi-currency and multi-market support 5 - Pricing systems or CPQ tools for contract and volume-based pricing
These integrations keep product data accurate and create a unified experience for both buyers and internal teams.
Can MagicFuse fix failed or slow B2B Commerce implementations?
Yes. MagicFuse specializes in recovering incomplete, slow, or unstable B2B Commerce rollouts. We audit data, optimize integrations, rebuild pricing logic, refine UX, and correct architectural issues that limit performance or scalability.
What’s the biggest mistake businesses make with Salesforce B2B Commerce?
The most common mistake is underestimating the importance of data structure and integrations. Poor catalog organization, inconsistent pricing data, and weak ERP connections create issues that impact every buyer interaction. Companies that invest early in clean product data, stable integrations, and UX design see far stronger results.
















