Salesforce Data Cloud is designed to unify and activate customer data at scale, leveraging its impressive processing power. Each Data Cloud instance operates within defined system limits that influence how organizations manage data, integrations, and performance.
However, beneath its flexible architecture lie defined limits and operational boundaries that every organization must understand. By recognizing how these limits affect data storage, processing, data actions, and integrations, businesses can prevent performance issues and ensure they are leveraging the platform to its full potential.
This article explores the major limits within Salesforce Data Cloud. It covers how limits differ by edition and license type, along with strategies to optimize performance while scaling your operations.
Editions, Licenses, and Usage Variability
Not all Salesforce Data Cloud organizations are created equal. Usage limits vary based on your edition, such as Professional, Enterprise, or Unlimited, and your type of license, like the Customer Data Platform or standard Data Cloud license, including the number of active users. Each influences the allowable data volume, API thresholds, processing caps, the number of rows and billable consumption.
Some limits are hardcoded into the platform and cannot be changed, while others are flexible and may be raised through contractual negotiation. Developer organizations, for example, have different limits that are generally lower and suited for testing environments. It’s essential to confirm your organization’s applicable thresholds and billing model before scaling operations.
Key Salesforce Data Cloud Limits
Data Storage and File Allocations
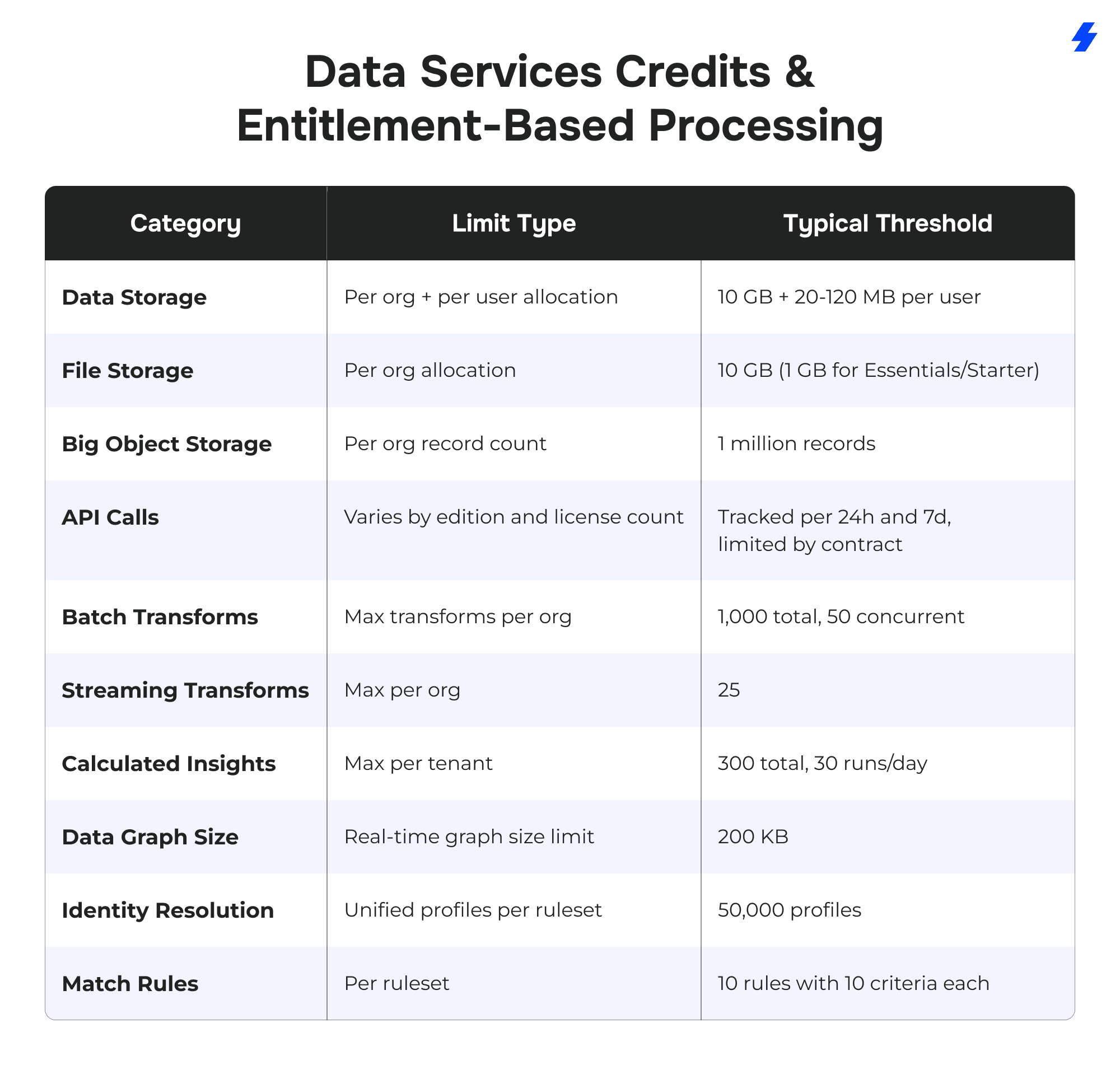
Salesforce categorizes storage into three primary types: data storage, file storage, and big object storage. These are measured and billed separately.
Data storage applies to records from standard and custom objects like Accounts, Contacts, Cases, and Opportunities, as well as various data sources. As of recent allocations, most editions offer 10 GB per org, plus additional per-user allocations (typically 20 MB for most editions, and 120 MB for Unlimited). Objects tied to Order Management are counted separately and allocated their own 50 MB for managed and unmanaged orders.
File storage includes assets such as attachments, CRM content, Chatter files, user photos, and Site.com resources. Salesforce typically grants 10 GB of file storage per org in most editions, while Essentials and Starter Editions are limited to 1 GB. Note that file storage for certain records or data types may consume more space based on data usage.
Big object storage allows for the retention of historical data across up to 1 million records per org, which can help to unify data. Though not actively monitored, Salesforce may enforce limits contractually if exceeded.
API Call Constraints
Salesforce Data Cloud offers robust API options, REST, SOAP, Bulk, Streaming, and Profile APIs, all subject to daily and monthly call limits. The total number of permitted API calls depends on edition, license count, and specific entitlements.
REST and SOAP APIs are commonly used for reading and writing data, while the Bulk API is best suited for high-volume batch operations, and the Streaming API is ideal for high-volume, real-time data streaming scenarios. Efficient use of API calls, for instance, in customer data activation, includes batching operations, minimizing round trips with composite requests, and leveraging caching to avoid redundant queries.
Salesforce provides two key tools to monitor API usage:
- System Overview – Displays total API calls made in the last 24 hours.
- API Usage Last 7 Days report (available in Salesforce Classic) – Details calls by user and day.
Data Processing Constraints: Understanding the Maximum Number of Jobs, Graphs, and Limits
Salesforce Data Cloud’s processing capabilities are constrained by architectural boundaries to ensure performance at scale.
- Batch transforms are capped at 1,000 per org, with no more than 50 running concurrently.
- Streaming data transforms, often used to power real-time streaming insights, are capped at 25 per org and must be under 20,000 characters per SQL statement.
- Calculated insights are restricted to 300 per tenant, with 30 manual executions per insight per day, and maximum runtime of 2 hours.
- Data graphs are constrained by size (200 KB for real-time graphs), record limits (up to 200 million in standard, 100 million in real-time), and object inclusion rules.
- Identity resolution is limited to unifying 50,000 source profiles per unified profile, and no more than 4 jobs per ruleset per day. Salesforce allows up to 50 match keys and 50 deduplication rules per tenant, with match rules containing up to 10 match conditions each. Careful design of rulesets and match keys ensures optimal profile unification and avoids unnecessary credit consumption. However, reaching these thresholds can introduce significant performance impacts, such as slower processing times or delayed job completion, which may lead to an overestimation of the system’s capabilities if not accounted for during planning.
Salesforce distinguishes between batch and real-time processing models.
Batch jobs, such as large-scale data transformations or profile unifications, are queued and processed according to system availability and job concurrency limits.
Real-time processes, such as streaming ingestion or immediate segmentation updates, are prioritized for low-latency use cases and operate under stricter limits to preserve performance.
Organizations should balance the need for real-time processing with system costs. Reserve real-time jobs for activities that truly require low-latency decision-making.
Data Services Credits and Entitlement-Based Processing
Beyond edition and license type, Salesforce Data Cloud operates on a usage-based model governed by Data Services Credits. These credits act as consumption units for various operations such as data ingestion, transformation, calculated insights, and identity resolution. Each processing activity, whether batch or streaming, draws down from your total credit pool.
Understanding how many credits your organization receives (per month or annually), how fast they’re consumed, and what activity uses them is essential to prevent unexpected slowdowns or cost overages.
Credits are tracked within the Admin Console and are allocated based on different operations such as data ingestion and identity resolution. If your organization approaches its allocated credits, additional purchases can be made to ensure continuous usage without performance degradation.
How to Optimize Usage and Stay Within Limits
Salesforce Data Cloud is engineered to scale, but without proper optimization, organizations may quickly run into processing delays, cost overruns, or system errors. Staying within platform limits requires a proactive approach, one that involves continuous monitoring, architectural foresight, and operational discipline. These measures also ensure that critical data actions, like segmentation, syncing, and identity resolution, continue to perform reliably at scale.
Monitor and Proactively Manage Consumption
Effective usage optimization begins with visibility. Salesforce provides several native tools to help organizations monitor their consumption of key resources, such as API calls, storage, and data processing workloads.
Administrators should configure dashboards that display real-time metrics from the System Overview panel, which shows daily API usage, storage utilization, and workflow queues. This view is especially useful for flagging abnormal spikes or degradation in performance.
For more advanced tracking, Event Monitoring and the Limits REST resource offer granular data on API activity, including the types of APIs called, frequency, source, and volume. Combined with automated alerts, these tools can detect thresholds approaching their limits before they impact the business. Using both short-term (24-hour) and historical (7-day or more) reports gives a balanced picture of current trends and usage patterns.
In Pardot (Account Engagement), users can also access graphical reports that show hourly API activity by module and action. This helps isolate usage surges tied to specific automation or integrations.
Archive Strategically to Reduce Storage Load
Storage limitations, particularly data storage, can be a hidden operational risk if left unmanaged. As data volumes grow, costs can increase and performance can degrade due to excessive object loads.
Salesforce recommends archiving infrequently accessed records rather than deleting them. Archiving preserves historical data for compliance or analytical use while freeing up active storage. Native tools, such as Salesforce’s Big Object architecture, allow long-term retention of structured data outside the scope of real-time performance workloads.
Big Object architecture in Salesforce is a data storage model designed to handle massive volumes of records, often billions, without affecting application performance. Unlike standard or custom objects, Big Objects store data in a compressed, non-transactional format optimized for retention and retrieval, not frequent updates.
They are indexed using a primary key (one or more fields) that defines how records are stored and queried. Access is primarily through SOQL queries with filters on indexed fields, ensuring efficient lookups even at very large scale. This makes Big Objects ideal for archiving historical data, storing event logs, or retaining records for regulatory compliance, while keeping the active org lean and responsive.
Optimize API Usage with Efficient Patterns
API call limits are one of the most common bottlenecks for organizations with integrated systems or high-frequency data flows, especially concerning the number of streaming API call . Poor API design, such as overly granular calls, unnecessary refreshes, or real-time dependency chains, can lead to API exhaustion and throttling.
To mitigate this, developers should prioritize batching logic where possible. The Bulk API is optimized for large data volumes and reduces the number of HTTP requests by grouping records into a single operation. Similarly, Composite API requests allow multiple updates or queries to be bundled and executed sequentially or in parallel, reducing call overhead.
Client-side caching can also significantly reduce redundant calls. For example, lookups to reference data (like pricing tables or status lists) should be cached locally rather than fetched with each transaction. Scheduled syncs, instead of continuous polling, help reduce load when real-time data isn’t strictly necessary.
Salesforce also offers event logs and rate-limit monitoring tools that provide insights into API call origins, helping teams fine-tune or re-architect inefficient integrations.
Cleanse and Deduplicate Data
The volume of data in Salesforce environments often grows faster than its quality. Unclean data can skew analytics, increase API load, and hinder segmentation efforts.
Organizations should implement automated data validation rules to enforce entry standards at the point of creation. This includes ensuring mandatory fields are filled, formats are correct, and lookup relationships are properly mapped. Field-level validations also support compliance and help maintain consistency across user-entered records.
Regular deduplication is equally important. Tools like Salesforce Matching and Duplicate Rules help prevent duplicate records from being created, while third-party applications offer more advanced merging, scoring, and cleansing capabilities.
An effective data hygiene strategy includes scheduled data audits, segmentation checks, and dashboard-driven quality scoring. Teams should evaluate data quality across multiple metrics such as completeness, uniqueness, timeliness, and accuracy, aligning with Salesforce’s best practices for customer data platforms.
Streamline Data Modeling
A common performance trap in Data Cloud environments is overly complex or unoptimized data modeling. Excessive field counts, deeply nested object relationships, or unnecessary calculated insights can overwhelm the system and lead to query timeouts or delayed graph refreshes.
To avoid these issues, businesses should limit data model objects to what is strictly necessary for business logic, personalization, or analytics. Salesforce enforces limits on both the number of fields per object (up to 1,050) and the total number of data model objects (7,500 per org). Staying below these thresholds is not just about compliance; it’s about maintaining speed and usability.
When building data graphs or segmentation models, aim to reduce the number of joined objects and avoid including fields or insights that are not directly used in decisioning or activation. Real-time graphs, in particular, should be kept lean and focused to stay within the 200 KB size limit and preserve their refresh frequency.
Competitor Analysis: Salesforce Data Cloud vs. Other Data Platforms
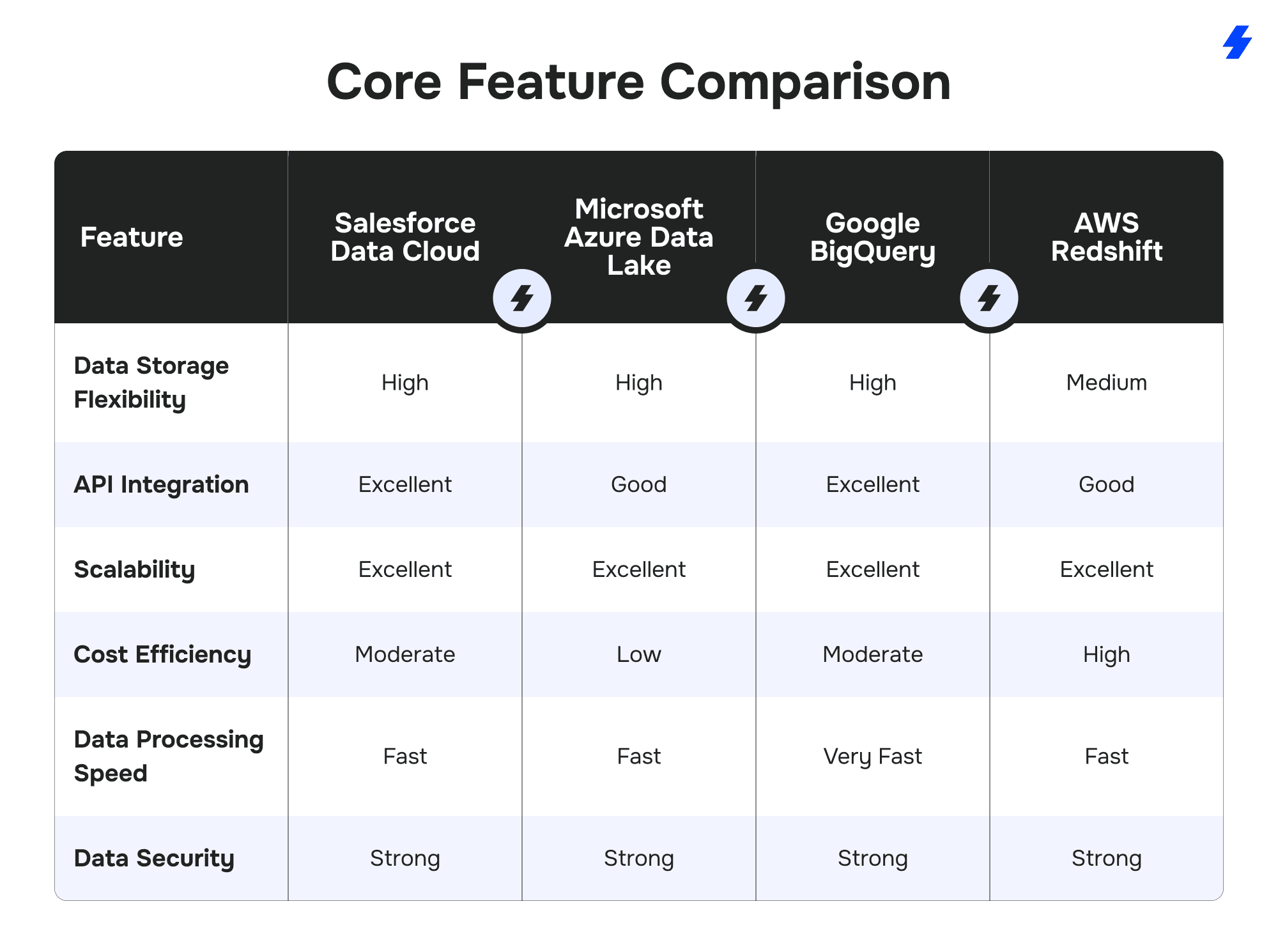
Salesforce Data Cloud operates in a competitive landscape alongside prominent data management platforms such as Microsoft Azure Data Lake, Google BigQuery, and AWS Redshift.
While all these platforms offer robust data storage, processing, and integration capabilities, Salesforce Data Cloud distinguishes itself through its deep alignment with the Salesforce ecosystem and its real-time customer-centric architecture.
Unlike general-purpose data lakes that rely on flat files or raw data lake objects, Salesforce Data Cloud allows customer-centric modeling and activation directly within the CRM ecosystem.
Core Feature Comparison
The following table outlines how Salesforce Data Cloud compares with its leading counterparts across several key dimensions:
Native Salesforce Integration: A Strategic Advantage
What sets Salesforce Data Cloud apart is its seamless integration with other Salesforce products, including Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, and MuleSoft. This native interoperability creates a unified ecosystem that significantly reduces integration overhead, development time, and synchronization errors.
Unlike general-purpose data lakes or warehouses, Salesforce Data Cloud is purpose-built for managing customer-centric data in real time. It natively understands Salesforce objects, permissions, and sharing models, enabling instant access to insights without the need to flatten, replicate, or re-architect CRM data into another environment. For Salesforce users, this reduces complexity and accelerates time to value.
Furthermore, Data Cloud’s real-time identity resolution and segmentation capabilities provide a higher level of personalization, enabling unified profiles and automation, which is difficult to replicate in traditional cloud warehouse platforms without significant customization.
Cost Efficiency for Salesforce-Centric Organizations
For organizations already invested in the Salesforce ecosystem, Data Cloud offers a more cost-effective alternative to building a data warehouse from scratch or integrating multiple third-party systems. Because the infrastructure, APIs, and data models are already aligned, businesses avoid additional licensing, transformation, and engineering costs commonly associated with external platforms.
While the cost-per-gigabyte for storage may be higher compared to solutions like Azure Data Lake, the total cost of ownership for mid-sized businesses, particularly those focused on customer engagement, marketing automation, and sales enablement, is often lower when factoring in reduced development and maintenance time. Salesforce also offers Data Cloud Starter plans that lower the barrier to entry, making it more accessible for small businesses or pilot implementations.
Salesforce Data Cloud is particularly well-suited for small to mid-sized enterprises that prioritize speed, agility, and alignment with go-to-market teams. For these companies, the ability to rapidly activate unified profiles across marketing, sales, and service can lead to faster ROI than traditional data lake architectures designed primarily for technical or engineering teams.
Strategic Considerations
Choosing between Salesforce Data Cloud and platforms like BigQuery or Redshift should be guided by business goals, existing technology stack, and data maturity. Organizations with diverse data types, advanced analytical needs, or existing investments in Google or AWS infrastructure may find external platforms more customizable. However, for businesses focused on customer data activation and already leveraging Salesforce, Data Cloud offers unmatched convenience, speed, and integration.
Best Practices for Long-Term Optimization
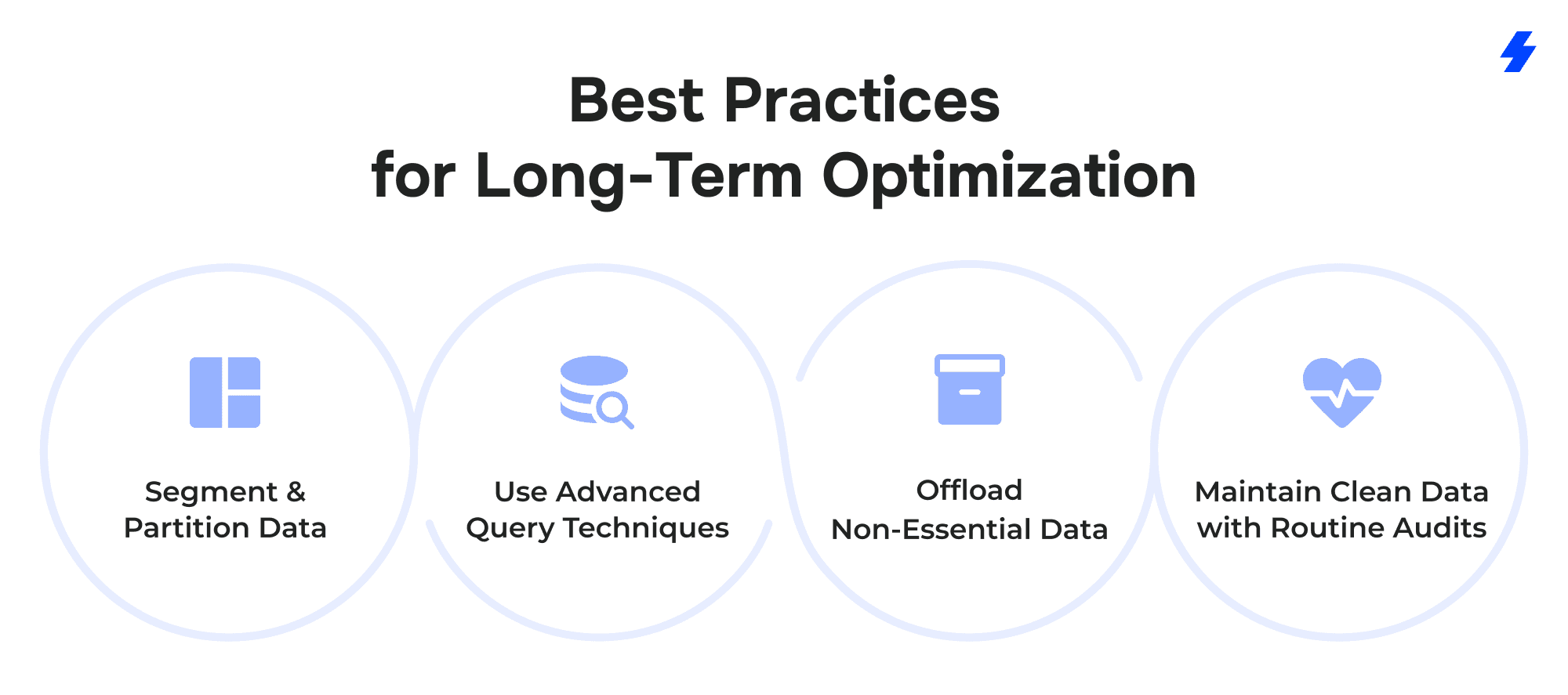
Segment and Partition Data
Segmenting data not only improves performance but also ensures relevant records are retrieved in queries and visualizations. Use data partitioning within data graphs and segmentation tools to break down large datasets into manageable, actionable subsets.
Use Advanced Query Techniques
Complex queries should be optimized to avoid long response times or API timeouts. Use pre-filtering in hybrid search, nested SOQL where applicable, and limit data retrieval to only necessary fields.
Offload Non-Essential Data
Integrate with third-party platforms such as MuleSoft to offload infrequently accessed or legacy data into external systems. This reduces strain on your active Data Cloud environment without sacrificing access.
Maintain Clean Data with Routine Audits
Implement weekly or monthly routines to audit fields that have been created, identify duplicates, and review validation rules. Establish data quality dashboards to monitor completeness, accuracy, and consistency. Over time, these routines improve usability and reduce unnecessary load.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
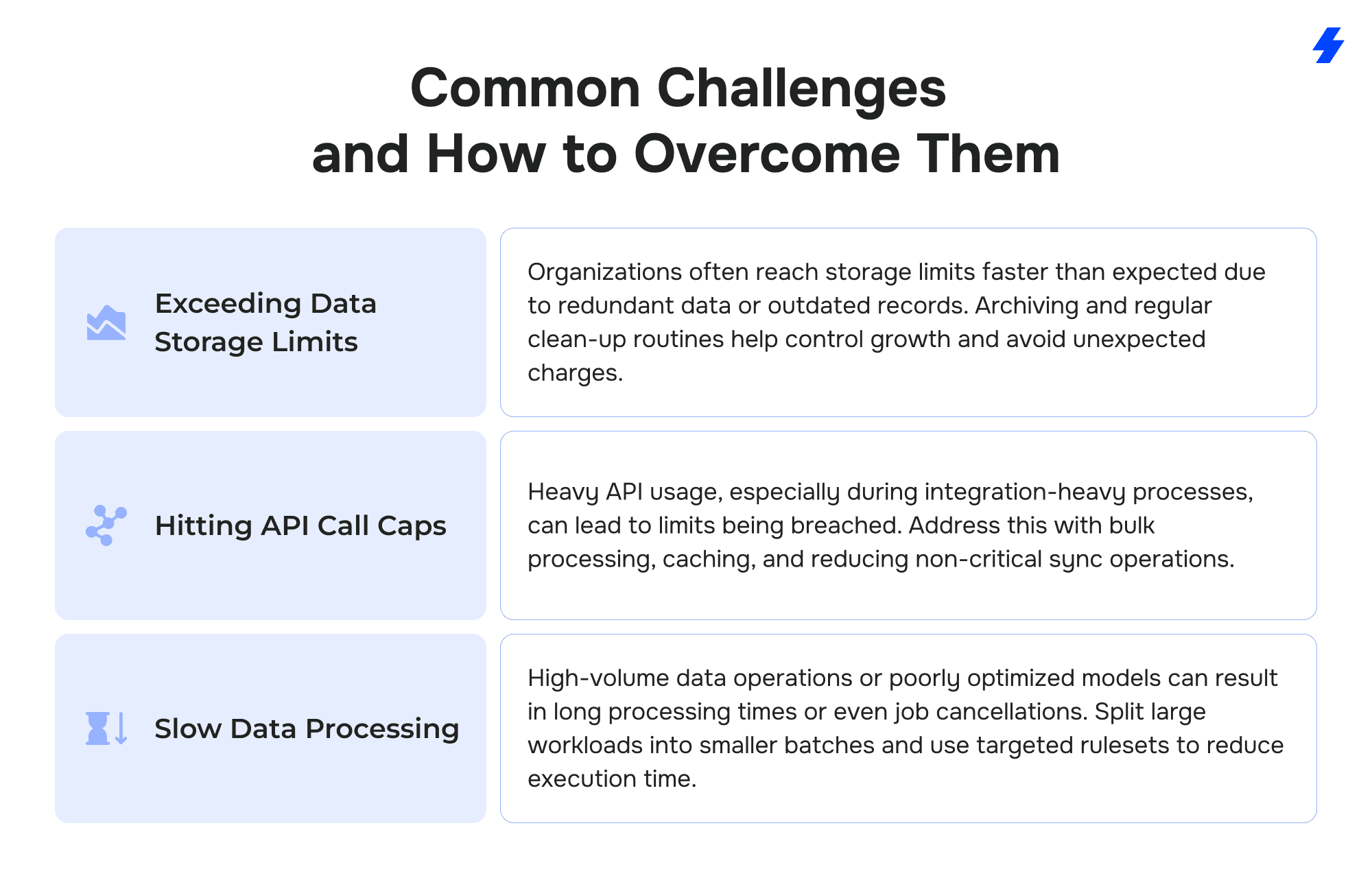
Challenge: Exceeding Data Storage Limits
Organizations often reach storage limits faster than expected due to redundant data or outdated records. Archiving and regular clean-up routines help control growth and avoid unexpected charges.
Challenge: Hitting API Call Caps
Heavy API usage, especially during integration-heavy processes, can lead to limits being breached. Address this with bulk processing, caching, and reducing non-critical sync operations.
Challenge: Slow Data Processing
High-volume data operations or poorly optimized models can result in long processing times or even job cancellations. Split large workloads into smaller batches and use targeted rulesets to reduce execution time.
Why Choose MagicFuse for Salesforce Data Cloud Integration?

100% Certified Team
Our entire engineering team holds Salesforce certifications, ensuring expert-level knowledge and proven skills to deliver reliable, high-quality solutions.
250+ Salesforce Certifications
With over 250 certifications earned, including recent ones like Experience Cloud Consultant, Data Cloud Consultant, B2B Solution Architect, AI Specialist, and more, we stay at the forefront of Salesforce innovations to meet your evolving needs.
Customer-Facing Engineering Team
We believe in full transparency. Our clients have direct access to our engineers and resources, with no hidden layers, enabling smooth communication and collaborative problem-solving.
Fast Recruitment & Strong Retention
We recruit top Salesforce experts quickly, averaging 6 weeks per hire, while maintaining strong employee retention of over 3 years to provide consistent expertise on your projects.
Outstanding Client Satisfaction
Our commitment to quality is reflected in an impressive Net Promoter Score of 92%, showing that clients trust and recommend our services.
Top AppExchange Rating
With a stellar 4.9-star rating on Salesforce AppExchange, we demonstrate consistent excellence and customer satisfaction in the Salesforce ecosystem.
Contact the MagicFuse team to explore how we can help you implement, optimize, and scale your data strategy.
FAQs
What are the main limits in Salesforce Data Cloud?
Limits include data storage caps, API request quotas, constraints on data graphs, constraints on the number of rows and the maximum number of data transform executions. These vary by edition and license.
How can I optimize my Salesforce Data Cloud usage to stay within limits?
Monitor consumption, archive data, streamline models, reduce API calls, and perform regular data cleanups.
What strategies can help me manage large datasets in Salesforce?
Use batch processing, partition data graphs, optimize queries, and offload infrequently accessed records.
Can MagicFuse help me integrate Salesforce Data Cloud with other platforms?
Yes, MagicFuse specializes in complex integrations including MuleSoft, Marketing Cloud, and third-party CRMs.
What tools does Salesforce provide for monitoring Data Cloud limits?
System Overview, API Usage Reports, and Event Monitoring provide visibility into storage, API activity, and data health.
What are source records in Salesforce Data Cloud?
Source records refer to the original data entries imported into Salesforce Data Cloud from external data sources like CRMs, marketing tools, or transactional databases. These records serve as the foundation for identity resolution, segmentation, and profile unification. Maintaining high-quality source records is essential for accurate insights and effective personalization.